Graphical Representation of Break-even Analysis Chart, Graph
Alternatively, if the selling price per unit increases from $25 to $30 per unit, both operating income and the contribution margin ratio increase as well. Variable cost per unit remains at $10 and fixed costs are still $8,000. Businesses can use the contribution margin to make informed decisions about pricing, product mix, and resource allocation. For example, the company could use the contribution margin to determine the profitability of a new product line or to analyze the impact of changes in selling prices or variable costs. By analyzing variable costs in CVP analysis, businesses can make informed decisions about pricing, product mix, and resource allocation. For example, the company could use CVP analysis to determine the impact of a price increase on its profits or to decide whether to produce and sell a new product line.
Which of these is most important for your financial advisor to have?
The focus may be on a single product or on a sales mix of two or more different products. For example, if unit selling prices, unit variable costs, and total fixed costs remain constant, the P/V graph can show how many units must be sold to achieve a target profit. Cost-Volume-Profit (CVP) analysis is a managerial accounting technique which studies the effect of sales volume and product costs on operating profit of a business. It shows how operating profit is affected by changes in variable costs, fixed costs, selling price per unit and the sales mix of two or more products. Cost Volume Profit (CVP) analysis is used in cost accounting to determine how a company’s profits are affected by changes in sales volume, fixed costs, and variable costs. Various techniques are involved, including the calculation of the contribution margin and the contribution margin ratio, the break-even point, the margin of safety, and what-if analysis.
Contribution margin income statement
Our goal is to deliver the most understandable and comprehensive explanations of financial topics using simple writing complemented by helpful graphics and animation videos. Our team of reviewers are established professionals with decades of experience in areas of personal finance and hold many advanced degrees and certifications. As a control technique, CVP analysis is used to measure the performance of the different departments in a company. CVP analysis is a tool used extensively in both the planning and control functions of an organization. The great thing about a CVP graph is that you can highlight the points and figures most important to your company.
Difference Between Cost Volume Profit Analysis And Break Even Analysis
The contribution margin can be used to cover the company’s fixed costs and generate a profit. If the store sells $20,000 worth of merchandise in a month, the variable costs, such as the cost of goods sold, maybe $10,000. The contribution margin, which is the difference between the sales revenue and the variable costs, would be $10,000. This means that the company needs to sell 2,000 widgets to cover its fixed costs and break even. If the company sells less than 2,000 widgets, it will incur a loss; if it sells more than 2,000 widgets, it will profit. The contribution margin income statement is usedquite frequently since it separates fixed and variable costs toallow a company to see what it can directly change and what itcannot change.
What is Cost Volume Profit (CVP) Chart?
A decrease in unit selling price would also decrease this ratio, and a decrease in unit variable cost would increase it. Any change in fixed costs, although not illustrated in the examples, would not affect the contribution margin ratio. Total revenue is $ 120,000 for salesof 6,000 tapes ($ 20 per unit X 6,000 units sold). In the chart, wedemonstrate the effect of volume on revenue, costs, and net income,for a particular price, variable cost per unit, and fixed cost perperiod. To illustrate the concept of contribution margin in CVP analysis, let’s consider the example of a company that produces and sells widgets. The company has a selling price of $10 per widget, and its variable costs are $5 per widget.
Fixed costs remain constant regardless of production levels, whereas variable costs fluctuate with the production volume. In summary, the contribution margin is the amount of revenue left over after variable costs have been deducted from the sales price of a product. It is an important concept in Cost-Volume-Profit (CVP) analysis and can help businesses make informed decisions about pricing, product mix, and resource allocation. To illustrate the concept of the break-even point in CVP analysis, let’s consider the example of a company that produces and sells widgets. The company has fixed costs of $10,000 per month, and its variable cost is $5 per widget. The break-even point is a key concept in Cost-Volume-Profit (CVP) analysis.
- This, as a result, facilitates adaptability to changing market conditions.
- Cost-volume-profit (CVP) analysis, also referred to as breakeven analysis, can be used to determine the breakeven point for different sales volumes and cost structures.
- This video will give you an example of the why andhow to do a contribution margin income statement.
- In summary, the sales price is an important component of Cost-Volume-Profit (CVP) analysis.
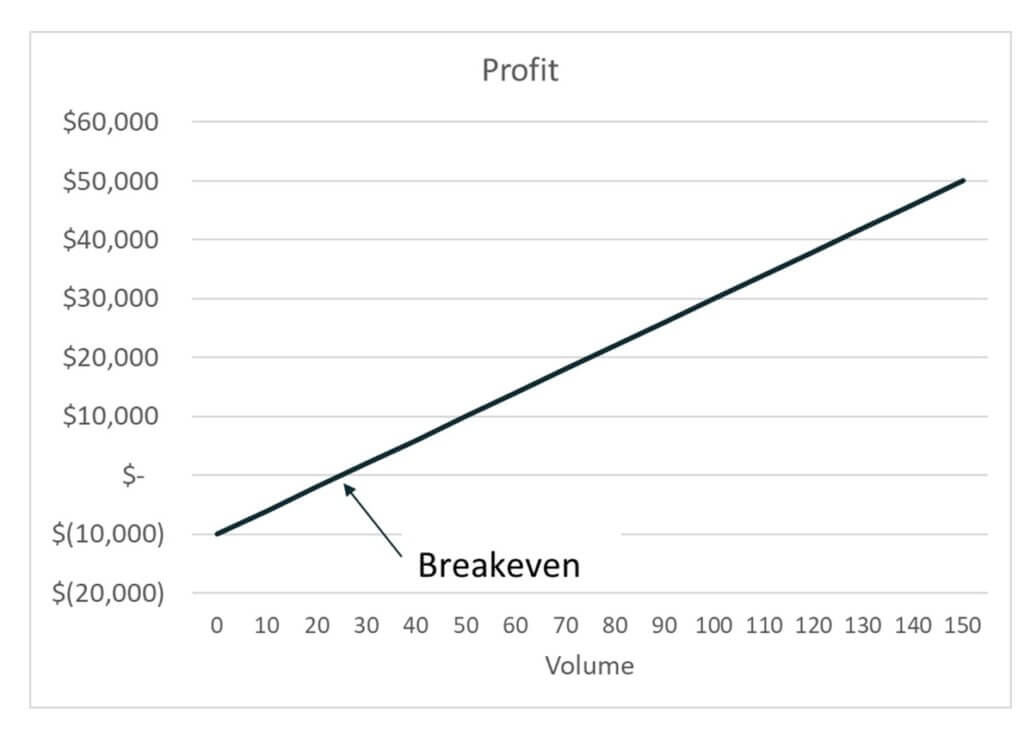
Contribution margin is the amount by which revenue exceeds the variable costs of producing that revenue. Below and to the left of the break-even point, the difference between the total cost line and the total revenue line reflects the net loss for the period. CVP analysis shows the relationships among a business’s costs, volume, and profits. It’s a simple and straightforward analysis that can be a useful starting point when you’re doing your calculations and may give you handy jumping-off points as you start to refine your plans.
The unit contribution margin is simply the remainder after the unit variable cost is subtracted from the unit sales price. Cost-volume-profit (CVP) analysis, also referred to as breakeven analysis, can be used to determine the breakeven point for different sales volumes and cost structures. The breakeven point is the number of units that need to be sold—or invoice templates for word and excel the amount of sales revenue that has to be generated—to cover the costs required to make the product. A CVP analysis keeps calculations simple – but that means it has to make some assumptions upfront. For example, a CVP analysis assumes that all the units you produce will be sold and also assumes that your fixed and variable costs are constant.
Performing the CVP, we calculate the Break-even point for various sales volume and cost structure scenarios, to help management with the short-term decision-making process. As it focuses mainly on the Break-even point, it is commonly referred to as Break-even Analysis. The difference between total sales revenue and total variable costs, representing the portion of sales that helps to cover fixed costs. The contribution margin is part of the formula used to determine the breakeven point of sales. By dividing the total fixed costs by the contribution margin ratio, the breakeven point of sales—in terms of total dollars—may be calculated. For example, both the fixed cost per unit and the variable cost per unit are considered to be constant, and so is the sales price.
I am a finance professional with 10+ years of experience in audit, controlling, reporting, financial analysis and modeling. I am excited to delve deep into specifics of various industries, where I can identify the best solutions for clients I work with. Computing the break-even point is equivalent to finding the sales that yield a targeted profit of zero. The first step required to perform a CVP analysis is to display the revenue and expense line items in a Contribution Margin Income Statement and compute the Contribution Margin Ratio.
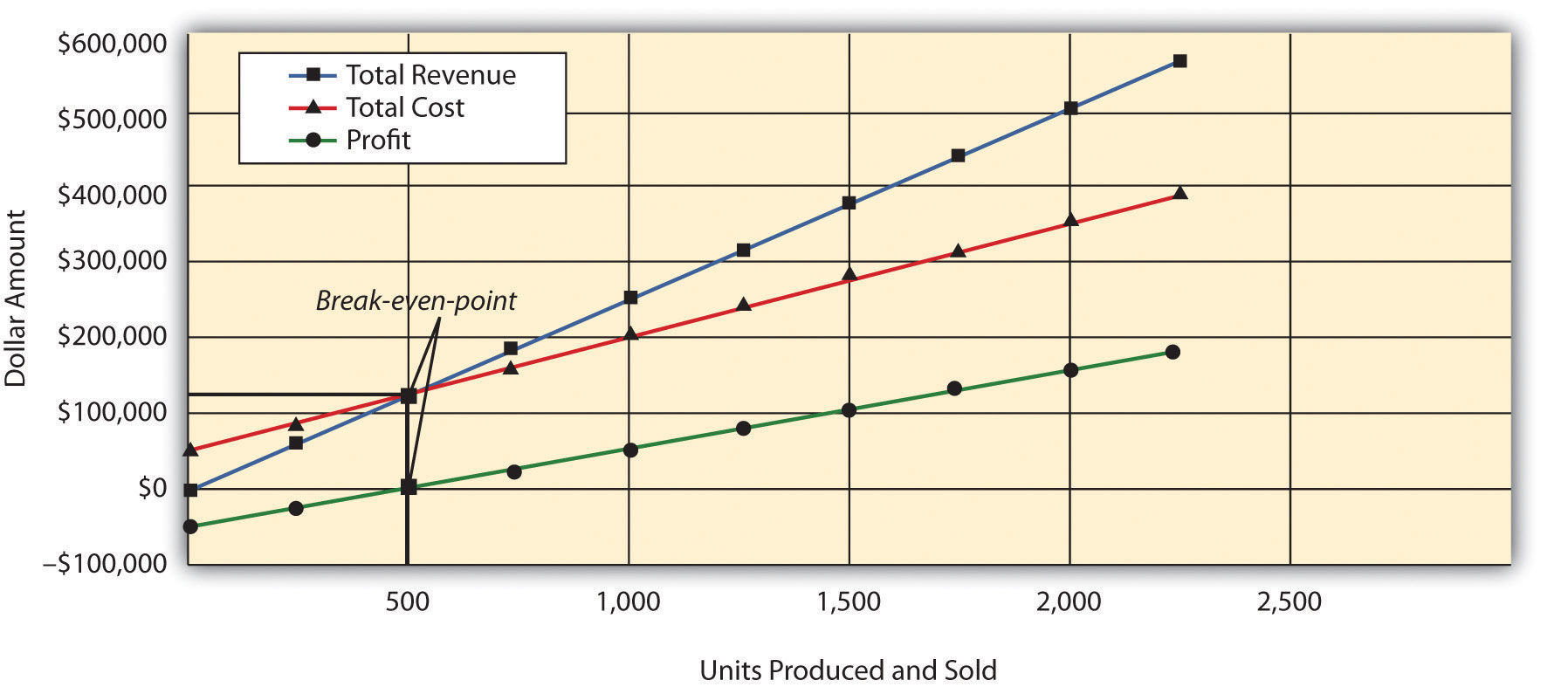
It allows you to analyze the relationship between costs, volume, and profit. This enables you to optimize your business’s operations and plan for the future. Cost-volume-profit (CVP) analysis is a method of evaluating the impact that varying levels of costs and volume have on a company's operating profit. The vertical axis shows total profits or losses, while the horizontal axis represents units of product and sales revenue. The total cost line is the sum total of fixed cost ($3,000) and variable cost of $15 per unit, plotted for various quantities of units to be sold. Moreover, CVP analysis can help businesses determine the most profitable mix of products and the most effective sales strategies.






